
Climate change has a significant impact on human and animal health. It is crucial for citizens to be aware and prepared for the potential health dangers that climate change may present.
Climate change can have a significant impact on many health issues, including respiratory disease, foodborne illness, and vector-borne diseases. Climate change can increase the likelihood of very large fires in some parts of the world like the West. Also, people are more vulnerable to asthma and allergic reactions.
Heatwaves are one of the most dangerous climate-related threats to human life. Studies have shown that heat waves with higher frequency are associated with more heat-related deaths as well as complications from cardiovascular and respiratory conditions. Higher risks exist in areas where people are outdoors.

In addition to heat-related diseases, people may be at risk from floods, storms, and other extreme events. These events may contaminate water with bacteria or other harmful chemicals. These events may also result in food-borne illnesses such as cholera. Dehydration and severe diarrhea can occur.
Climate change will, among other effects, make air pollution worse. Fossil fuels will cause an increase in ground level ozone, and smog. Increasing levels of these pollutants are predicted to exacerbate allergy conditions, cardio-respiratory problems, and other respiratory diseases.
Indirect effects of climate changes can have a negative impact on human health. They include the occurrences of infectious diseases like West Nile virus, cholera, and malaria. Changes in pollen and ragweed may lead to an increase in seasonal allergies. And, of course, more frequent and intense storms will wreak havoc on water and land.
Vulnerable populations include children, infants, pregnant women and older adults who are particularly vulnerable to climate-related effects. Their location, along with their medical and age, will impact their ability to adapt to the climate change hazards.
Indigenous Peoples of USA are among the most vulnerable. They live in poor, isolated communities. They rely on the environment to provide their sustenance.
While the majority of Americans are aware there is a danger from climate change, not all are conscious of how it could affect their health. The most vulnerable are older adults, minorities and people with preexisting conditions.
PAHO's Climate Change and Health Program was created to address the health consequences of climate change. This program seeks to reduce greenhouse gases emissions and promote health-oriented, climate change adaptation measures. PAHO also plans to give awards to tribal governments, territories, and other entities that prepare for and responds to the health consequences of climate change.
Although different people experience climate change in their own ways, there's no doubt that it will have major impacts on our health. It is estimated that the U.S. will experience thousands of premature mortality by the year 2025, with many more deaths globally. Those in the most vulnerable groups will be at the greatest risk of suffering from climate-related health impacts.
FAQ
What happens to developing countries when they experience the climate change effects?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields. This will impact communities with low incomes and food insecurity. Extreme weather events such as hurricanes or heatwaves may cause damage to infrastructure and the displacement of people. This can further perpetuate economic inequality.
The long-term implications of climate change include continued resource scarcity, poverty, and health impacts including an increased number of vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue fever. There will also be an increased risk of flooding from rising sea levels, combined with extreme weather events. This puts lives at risk in coastal locations where many people lack the necessary infrastructure and emergency services to evacuate. To build resilience against these risks, mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions is necessary. Other measures include improved management and better access to water resources.
How does climate change affect extreme weather events?
Global warming is directly responsible for extreme weather events such as heat waves and floods, droughts. Cyclones, storms and hurricanes are all a result of global warming. Global warming has led to increased atmospheric temperatures.
According to climate scientists, the frequency of extreme weather-related catastrophes has more than doubled in the past 20 years. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This has an impact on the normal distribution and strength of hurricanes and storms across different regions of the planet.
The 2015 El Nino event caused warm water to move towards South America, leading to rising temperatures at alarming rates and heavy rains that caused floods in Peru (and Bolivia) causing property damage and displacement. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that humans are increasing the severity and frequency of climate change. This naturally leads to more severe, frequent, and intense natural catastrophes worldwide. It also provides strong evidence about human involvement in extreme weather events that occur at regular intervals around us all.
What is the climate impact of land use and deforestation?
The climate can be directly affected by deforestation and changes in land use. The trees that have been cut down or burned can no longer absorb carbon dioxide, one of Earth's most important greenhouse gases. The atmosphere is less carbon dioxide if trees are removed by deforestation, or burned for agriculture purposes.
At the same time, changes in land use can also release more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. To illustrate, if forests are replaced with agricultural lands to support livestock production, fertilizer and pesticide use could increase methane emissions. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
The effects of land-use change, deforestation, and increased greenhouse gas emissions can have a negative impact on the quality of regional air. The smoke from deforestation's burning events has been linked to poor visibility and other health concerns, such as asthma or other respiratory diseases. The cumulative effects of these changes in local air quality could have an impact on global climate change. Higher temperatures can be caused by more sunlight reaching the Earth's surface due to lower aerosol particles.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Temperatures are increasing dramatically due to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide, which is leading to heat waves, droughts and changes in rainfall patterns.
These changes are already having a profound affect on ecosystems worldwide, causing extinctions or disruptions of habitats. They are also threatening the lives and livelihoods of billions of people, particularly those in areas already facing resource scarcity and poverty.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. As temperatures rise, this trend will likely continue.
A rapidly changing climate has many effects. They can impact everything from food insecurity to displacement by extreme weather events to sea level rise, causing communities to relocate. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
Climate Change can have broad impacts on society as well as the environment. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
One of the most prevalent effects of climate changes worldwide is the rise of ocean levels as a result of melting ice cap. This can lead to shoreline erosion and increased flood risk for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events result in mass destruction of homes or businesses and can lead to relocation or complete loss of life. Additionally, severe storms pose additional risks due to flooding or landlides that can increase damage to infrastructure such roads and railways.
Additionally, wildfires caused climate change are more common than ever. They can be devastating for both the habitats and the people who live nearby.
Many people are forced to flee their homes due to drastic changes in their living conditions.
The increase in aridity causes dust storms to become more frequent, which makes people suffering from asthma and other respiratory ailments such as asthma even more vulnerable. Additionally, pest infestations are likely to rise significantly in conjunction with higher temperature extremes (a phenomenon known as the "greenhouse bug") which can cause further damage to agricultural production. This could further affect global food security numbers. As fewer crops become available at poorer nutritional qualities, it may bring additional hardships on marginalized communities already struggling to make ends meets otherwise.
How does climate change affect the world's oceans and marine life?
What are the effects of climate change on oceans and marine life around the globe?
Since its inception climate change has significantly affected the world's oceans as well as the marine life associated with them. The depletion of the ozone layer, which causes constant oceanic warming, has caused major disruptions to marine ecosystems. This has led to coral bleaching and a decline in species.
Climate change also causes unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms. These extreme surges can be deadly for coastal areas. Changes in temperature can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels, which could cause "dead zone" conditions in which marine life is scarce.
Ocean acidification is also caused by carbon dioxide that is released into the air and then accumulates in the seas. Ocean acidification causes an increase in pH which affects the vital functions of animals such as crabs, clams, and oysters that cannot adapt to changing conditions.
Higher temperatures can also cause changes in natural habitats. They may shrink or change their geographical location, making it unhabitable for species that depend on them. An increase in ocean pressure can cause a drastic imbalance between predators & prey and lead to the extinction of many species.
All ecosystems are affected by climate change. This can be directly or indirectly via evaporation, water volume reductions or sharp temperature shifts. These changes could have a devastating effect on sustainable development of marine activities and fisheries. Climate change is transforming the future of all life forms on our planet, not just those living on land but those living below the ocean surface.
How can we address climate change by addressing the role of the energy industry?
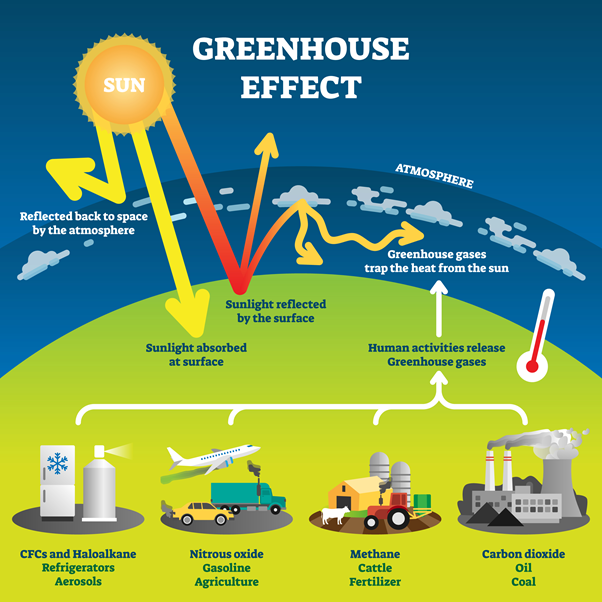
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. Global warming can be caused by the burning fossil fuels. The atmosphere releases carbon dioxide, trapping heat and leads to an increase in Earth's temperature.
To address this issue, energy sources must transition away from carbon-emitting fuels like coal and natural gaz and instead turn to renewable energy sources like solar, geothermal, wind, and other renewable sources. This transition can be made through both government policy and incentives, as well as investments in innovative technology like hydrogen fuel cell. Businesses and homeowners can cut their emissions while reducing their electricity bills by investing in infrastructure that supports these renewable sources.
Other methods include transitioning away from polluting transportation options like petroleum-fueled cars and moving towards electric vehicles or public transport. It is possible for governments to support battery technologies research and encourage people to use cleaner transportation.
Green business practices are essential to help reduce carbon emissions. Companies should implement better insulation systems in their offices, and energy efficiency plans in production facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must not only be supported at the company level, but also at the federal level to be truly successful. Taxing pollution products increases individuals' willingness to adopt healthier practices. But this won't force them to compete with polluters. Instead, vouchers or subsidies for low carbon products will create a continuous market to support sustainability. To sum up, combating climate change will require a huge effort by both the private sector and the public. Switching to renewable energy sources and adopting sustainable practices are key elements to ensuring that future generations are impacted positively.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy and Support the Transition to a Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is renewable energy that doesn't emit greenhouse gases or produce polluting emissions. This includes technologies like solar photovoltaic and wind power, as well as hydroelectricity, geoelectricity, and hydrogen fuel cell. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
By purchasing shares in companies that are developing new technologies in the sector, investors can become involved in clean energy projects. This can include investing in publically traded stocks, mutual funds, and ETFs (exchange-traded funds) related to renewable energy. Direct investments in start-ups and venture capital projects can be an option for investors to help fund research and development of clean energy technologies.
Clean energy investment is a way to support innovation and reduce harmful emissions. This investment could also result in increased economic development, as it creates jobs for skilled labor and engineers related to the production renewable energy systems. Lastly, investing in clean energy can bring investors a financial return through tax incentives programs that encourage investments into green technologies, such as wind farms, solar panels, or biomass heat generation systems.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.