
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), an intergovernmental organisation, was established as part of the United Nations Environmental Programme in 1988. It is a global organisation that brings together scientists, policymakers, as well as other people to discuss the effects of climate change and to help find solutions. The IPCC's mission is to educate the public about climate change and suggest possible solutions.
The Panel is non-partisan and is made up representatives elected by governments. These government representatives choose qualified scientists to represent them at IPCC meetings. Representatives recruit experts to help with the preparation of reports. The Panel can also be populated by government scientists. This practice does not necessarily mean that the government endorses a scientist's views.
The IPCC structure has three working groups, each focusing on different aspects. One group works on the physical sciences, and the other two work on adaptation/mitigation. Each working group is headed by a Cochair. Both Co-Chairs also belong to the IPCC Bureau. They advise the chair about the selection and preparation of the meetings.
The Working Group I, which is the first, focuses on the physical science and impacts of climate change. It includes the Met Office Hadley Centre which is one of the top climate research centres worldwide.
The Working Group II examines the impact of climate change upon people and ecosystems. It also proposes ways to reduce climate change. Its members include the Australian Government, which manages the DFAT Trust Fund and contributes to IPCC decisions.
Working Group III, the third working group, studies mitigation options and examines the economic and human impacts of climate change. It is made up of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and other organizations.

Reports produced by the IPCC are prepared by volunteer groups of hundreds of scientists from around the globe. They analyze scientific literature and provide recommendations based off the most current research. An IPCC assessment report is a comprehensive review of current climate change knowledge. A report can also be published in four parts.
Summary for Policymakers (or the summary) is an overview of the complete IPCC report. This report is most often of interest to journalists and the general public. Everybody can access the IPCC report and they are reviewed by several experts. The IPCC collaborated closely with communication experts and practitioners to prepare the Fifth Assessment Report.
IPCC hosted an Expert Meeting on Communication in February 2016. IPCC made many recommendations regarding how to communicate effectively at this meeting. Some of these guidelines were adopted into the IPCC’s outreach activities, and the IPCC website.
In September 2019, the IPCC published the Special Report of Ocean and Cryosphere under Changing Climates. The IPCC will soon release its Sixth Assessment Report. (AR6) is an in-depth review of climate change information. The report will be published as a series, just like the previous assessment reports.
FAQ
What are some possible solutions to climate change, and how effective are these solutions?
Climate change is an urgent issue, and it requires immediate attention from government, business, and citizens. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, increased sea levels, and melting polar ice are clear warnings of a disrupted climate system. There are many solutions that can be used to combat this phenomenon. They range from technological solutions and behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions. A variety of technological solutions have emerged to combat climate change. These solutions include renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, which are reliable sources of clean energy without causing any adverse effects on the environment. Electric cars powered with renewable energy could dramatically reduce pollution in cities and replace petrol vehicles. Reforestation projects are another technological option that aim to increase carbon sequestration, soil and trees. They also provide coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable areas from rising ocean levels.
Simple behavioral changes can help reduce emissions and limit future climate disruption. So, for example, buying locally-produced goods reduces the transport costs associated with food transport. By using active or public transportation to transport your goods, you optimize your use of resources and bring down costs and air pollution. Also, insulation can be more cost-effective and help reduce the dependence on gas boilers in heating your home.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness of these solutions largely depends on how much producers commit themselves towards investing in green alternatives; currently, initiatives such as using electric Cars tend expensive when compared with petrol versions however economic incentives favoring green investments play an integral role in incentivizing alternative solution uptake otherwise these remain mostly dormant when exposed only market forces which cannot guarantee their utility over time try apart from increasing consumer awareness over time regarding their efficiency hence mandating alternative solutions via policy measures represents one way forward however this needs regulatory bodies willing committed enough engaging players involved further still nontechnological approaches work one level but solving global warming phenomena requires all parties involved tackling issue earnest together.
What role does the energy sector play in climate change? How can this be addressed?
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. Global warming is caused by the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This traps heat and causes an increase in Earth's average temperature.
To address this, energy sources must move away from carbon-emitting sources, such as coal and natural gas, and instead transition towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal. This transition can be made through both government policy and incentives, as well as investments in innovative technology like hydrogen fuel cell. Businesses and homeowners can cut their emissions while reducing their electricity bills by investing in infrastructure that supports these renewable sources.
Another option is to move away from polluting transport options such as petroleum-fueled vehicles and towards electric cars or public transport. The government has great power to help societies transition away from oil-based infrastructures. They can support research into battery technology and encourage consumers to invest in cleaner modes.
Green business practices are essential to help reduce carbon emissions. Companies should implement better insulation systems in their offices, and energy efficiency plans in production facilities. This can drastically reduce operational expenses while also improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. It is important to recognize that tackling climate change takes a lot of effort from both the private and public sectors.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate Change has broad effects on both the environment and society. Climate change is causing a variety of environmental problems, including rising temperatures, extreme weather, sea level rise, and reduced air quality. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. This is expected to get worse as global temperatures continue rising.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This can lead to shoreline erosion and increased flood risk for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Climate change is causing extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts and other severe weather to occur in many countries. These events lead to massive destruction of homes, businesses, and even the loss of whole communities. Extreme storms can also cause flooding and landslides, which increase the damage to infrastructure like roads and railways.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to become more frequent than ever before. This can have devastating effects on habitats as well as people living near them.
Such drastic changes in living conditions often result in displacement or even refugee crises when people move away from their homes either voluntarily or involuntarily because their towns have become too dangerous or no longer habitable given their altered climate conditions against which they cannot cope adequately.
An increase in aridity means that dust storms can occur more frequently, making people with asthma and other respiratory illnesses like asthma particularly vulnerable. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
What is climate and how does it affect us?
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing global temperatures to rise which leads to an array of changes in weather and climate. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
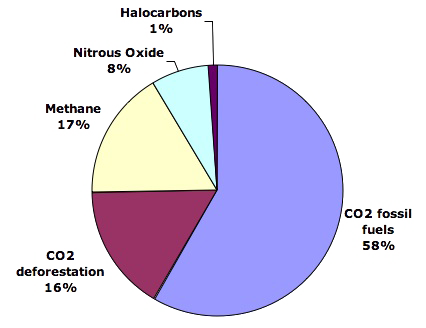
The main cause of climate change is human activity such as burning fossil fuels for electricity and transportation, cutting down forests, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
Deforestation also plays a large role contributing about 15-20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Forests also act as a natural carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere; without this absorption capacity, carbon dioxide levels around the globe will continue to rise, with disastrous consequences for ecosystems.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). Methane has been extensively employed in industrial processes. It contributes significantly to the atmosphere's warming. While N2O can be emitted primarily by agricultural soil management activities, such as tilling or fertilization which release excess nitrogen to soil.
To limit climate change, we must collaborate across economic, political, and social institutions in order to reduce our emissions and transition away fossil fuel dependence towards renewable energy sources. Smart solutions that encourage zero-waste living and replace polluting fossil fuels could help reduce atmospheric pollution and heat buildup. By taking responsibility for our impact on our environment we can begin mitigating damage through preservation measures like reforestation projects which help maintain biodiversity while absorbing large volumes of damaging CO2 back into nature providing powerful assistance in addressing the climate crisis and restoring balance for future generations
How do developing countries and communities experience the effects of climate change?
Due to their lack of access to resources, health care systems, and technology, communities and countries in developing countries are more vulnerable to climate change. Temperature, precipitation, sea levels, and rainfall changes put additional pressure on already scarce resources. Additionally, floods and droughts cause havoc in already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause decreased crop yields. This will have a significant impact on poorer communities suffering from food insecurity. Extreme weather events such as hurricanes or heatwaves may cause damage to infrastructure and the displacement of people. This can further perpetuate economic inequality.
Long-term consequences of climate change include increased resource scarcity and poverty as well as health effects such as an increase in vector-borne diseases like malaria or dengue fever. There will also be an increased risk of flooding from rising sea levels, combined with extreme weather events. This puts lives at risk in coastal locations where many people lack the necessary infrastructure and emergency services to evacuate. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to support climate-friendly policies and companies
Individuals can take several steps to support climate-friendly policies and companies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can also choose to switch providers to companies with a better environmental record, or opt for sustainable products over ones with higher carbon emission.
A key step to supporting climate-friendly policies is reducing one's carbon footprint. This may include changing daily habits such unplugging electrical appliances and switching off lights when not required, using environmentally friendly household products like biodegradable cleansers and composting kitchen soiled food scraps rather that putting them in landfills, wearing sustainable fiber clothing, choosing local foods whenever possible, installing energy-efficient energy systems at your home with solar panels or wind turbines, as well as planting trees around the property that absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
Before investing, investors who are interested in climate-friendly policies should look for companies that emit less carbon. They should review their portfolios on a regular basis to make sure that they are meeting the sustainability standards they have set. Green bond investors may be concerned that they do not invest in activities that emit more greenhouse gases than they take out. Investors should be alert to opportunities where funds can be converted towards green business activities like renewable energy alternatives or other initiatives promoting sustainability, such as community-building projects based on green technologies.