
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), an intergovernmental organisation, was established as part of the United Nations Environmental Programme in 1988. It is a global body that aims to bring scientists, policymakers and other people together to discuss climate change and to find solutions. The goal of the IPCC is to educate the world about climate change risks and offer possible solutions.
The Panel is composed of non-partisan representatives who have been appointed by the governments. These government representatives select qualified scientists for representation at IPCC conferences. Representatives recruit experts to help with the preparation of reports. A government can also nominate its own scientists for the Panel. This practice does not necessarily mean that the government endorses a scientist's views.
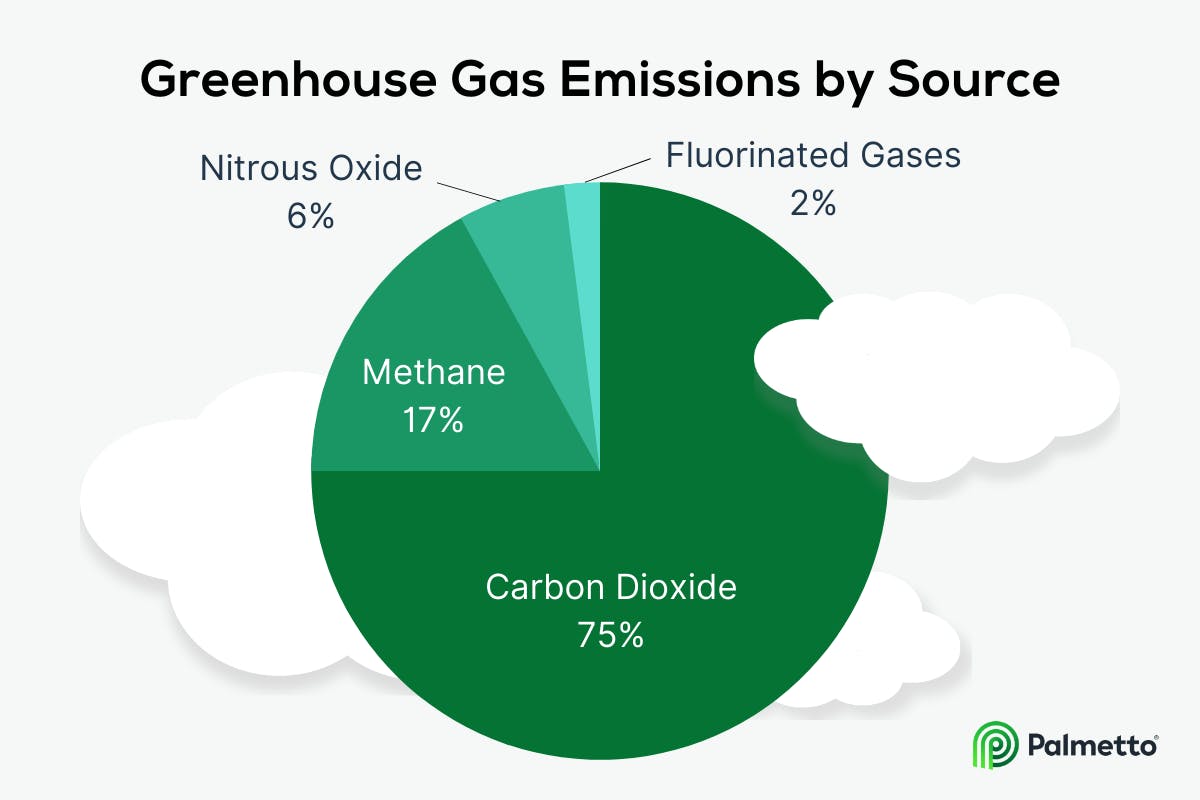
IPCC's structure consists of three groups that are focused on different aspects. One group works on the physical science, while the other two focus on adaptation and mitigation. Each working group is headed by a Cochair. Both Co-Chairs are members of the IPCC Bureau. They provide advice to the chair regarding the selection of authors as well as the preparations for meetings.
The Working Group I, the first of these groups, focuses primarily on the physical science behind climate change and its consequences. It includes the Met Office Hadley Centre - one of the most renowned climate research centres in the world.
The Working Group II examines the impact of climate change upon people and ecosystems. It also proposes ways to reduce climate change. The Australian Government is one of its members. It manages the DFAT Trust Fund, and contributes to IPCC decisions.
Working Group III, a third working group examines mitigation strategies and assesses the impact of climate-related changes on both the economic as well social dimensions. Its members include the World Bank, United States Agency for International Development, and other organizations.

The IPCC's reports are created by hundreds of scientists around the world in volunteer groups. They analyze scientific literature and provide recommendations based off the most current research. An IPCC assessment report provides a comprehensive overview of current climate knowledge. A report can be published in 4 parts.
A summary of the full IPCC report is called the Summary for Policymakers. This report is typically most useful to journalists and the public. All IPCC reports are open to the public and can be reviewed by a range of experts. For the Fifth Assessment Report, the IPCC worked with communications experts and practitioners.
IPCC held an Expert Meeting on Communication on February 16, 2016. At this meeting, IPCC adopted a number of recommendations on how to communicate effectively. Some of these ideas were integrated into the IPCC's outreach activities as well as the IPCC site.
In September 2019, the IPCC released the Special Report on Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. The IPCC is now preparing for the Sixth Assessment Report, (AR6). This report provides an extensive review of current climate-change knowledge. Like previous assessment reports, it will be released in parts.
FAQ
How can human activity impact climate change?
Climate change is a major contributor to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, humans have contributed more than 70% of global warming since mid-20th century.
Burning fossil fuels: Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels, such as oil and coal, are burned. This creates more atmospheric CO2, which acts like a "greenhouse" gas, trapping heat and increasing temperatures. This causes higher ocean levels, as Arctic ice melts. It also scrambles weather patterns across the globe, leading to dangerous storms, droughts, floods and other problems that can affect food production and human health.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Reduced forest cover can also increase albedo, which is the amount of reflected sunlight coming back into space. This reduces solar heat absorption at the surface of the earth and promotes global warming. Deforestation is also associated with respiratory problems and local air quality.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Due to the high levels of methane bacteria in animal waste, methane gas is released into the atmosphere in large quantities. Changing your diet to less or no animal products can help reduce this contribution. Smog from ground-level ozone can harm our respiratory system and make our lives more hazardous.
Conclusion: While human activity has had a significant impact on the environment over centuries, technology advancements such as renewable energy sources have allowed us to look towards the future. The results of these industries, which emit carbon, will soon be clear when we use technology through green innovations to make it eco-friendly and reduce climate change. All people are safe in a healthy, prosperous natural world.
What is the effect of land use changes and deforestation on climate?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. Trees that are cut down or burnt can no longer absorb carbon dioxide. This is one of the most important greenhouse gasses on Earth. Carbon dioxide is therefore less removed from the atmosphere when trees are deforested or burned for agricultural purposes.
However, land use changes can increase greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
Land-use and deforestation have more than just an increase in greenhouse gas emissions. They can also impact regional air quality. Deforestation can lead to reduced visibility, health issues such as asthma and other respiratory problems. The cumulative effects of these changes in local air quality could have an impact on global climate change. Higher temperatures can be caused by more sunlight reaching the Earth's surface due to lower aerosol particles.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
What is the relationship between climate change and extreme weather events?
Global warming is directly responsible for extreme weather events such as heat waves and floods, droughts. Cyclones, storms and hurricanes are all a result of global warming. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
Climate scientists claim that the frequency of extreme weather related disasters has more then doubled since 1980. Sea levels rise as a result of changing wind patterns and ocean temperatures. This has an impact on the normal distribution and strength of hurricanes and storms across different regions of the planet.
The 2015 El Nino event brought warm water toward South America. It caused alarmingly high temperatures and heavy rains, which led to flooding in Peru. These floods resulted in displacement of people and property destruction. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) concluded, "Human activities are increasing the severity current climate change." This naturally leads worldwide to more severe, intense, and frequent natural disasters. There is strong evidence of humans' involvement with extreme weather events occurring frequently around us all.
What's the current climate in the world? And how does it change?
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They are also threatening the lives and livelihoods of billions of people, particularly those in areas already facing resource scarcity and poverty.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
Global climate change is causing many problems. These include rising food insecurity, displacement due to extreme weather events and sea level rise that force communities to move. Climate change is also contributing to existing social inequalities. Itdisproportionately affects marginalized communities, which lack the resources and knowledge required to adapt.
There has been progress in some areas, such as the reduction of carbon emissions or initiatives for renewable energy in certain countries. However, there is no global initiative that can be taken to effectively mitigate these changes. For us to avoid further disruption and devastation due to climate change, all nations need to come together and take urgent actions now. At the same time, we must plan for adaptation in an uncertain world.
What is the potential of new technologies to combat climate changes?
New technologies have the potential to solve this global challenge. Advanced science is making it possible to shift to a more sustainable world.
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, new methods of carbon capture can be used. Enhanced agricultural practices can also help to reduce the amount of livestock and soil degradation. Smart grid technology can be integrated with existing power infrastructures to improve efficiency. Enhanced building design can help reduce energy consumption.
The latest synthetic biology methods allow scientists to create organisms that can use green sources of fuel like the CO2 laser as biofuels or alternative feedstocks. This could revolutionize transportation if the market turns away from petrol-based vehicles toward zero-emission electric cars powered by clean sources.
Finally, increasing investment in digital tech and AI can enable people to access data across borders and help them make more informed consumption decisions. Understanding how we contribute to the carbon production of our planet is key for better stewardship.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make Your Home more Energy-Efficient and Reduce Climate Change
Making your home energy-efficient is one of the best ways to reduce your carbon footprint, save money on utility bills, and make life more comfortable.
You must ensure that your home is properly insulated. You should ensure windows and doors are correctly installed, check for drafts around pipes, vents, and add weather stripping where needed.
Insulate your floors, ceilings, & walls for maximum energy efficiency. Make sure to inspect the attic and any other areas in your home for air leaks.
Lighting can account for as much as 18% of household electricity consumption. Make sure to switch to LED bulbs, which consume up to 80% less electricity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Installing motion sensors and timers will also help you save additional money by turning off lights as needed.
A newer model is more efficient and can help reduce your energy bills. A programmable thermostat allows you to control the temperature based on who is home and who is away.
All windows should be replaced by double-glazed units that are more energy efficient and less heat escaping. Look into buying low-flow showerheads which reduce water consumption while maintaining adequate pressure levels.
Replace appliances with ENERGY STAR rated products since they use up to 50 % less power than non-certified models. Make sure to take care of the little details, such as unplugging TV boxes and phone chargers when not in use. This could help save you significant energy.
These simple steps can reduce your impact on the climate and help you live more efficiently at home.