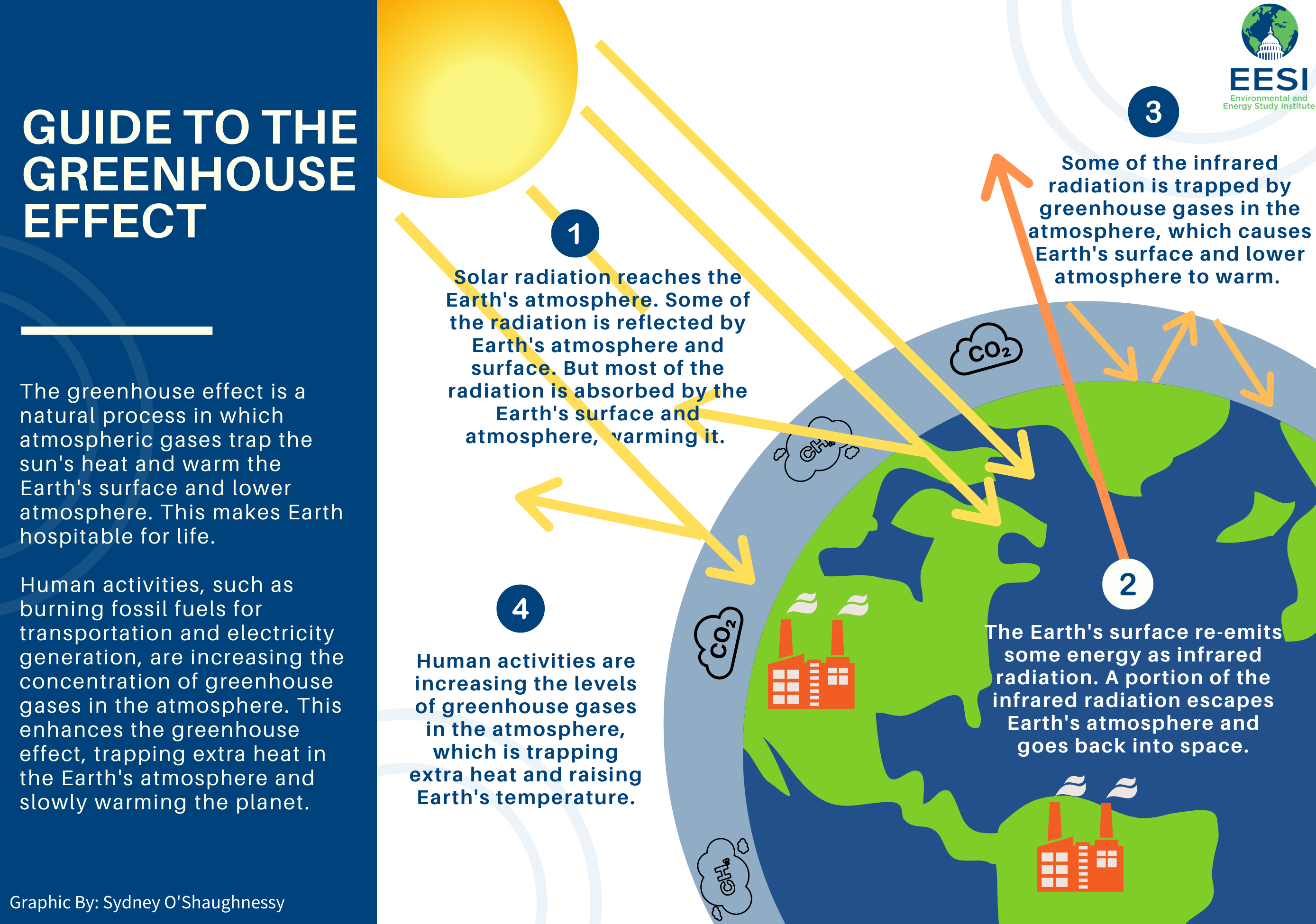
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 13(SDG 13), aims at reducing climate change impacts. This goal focuses on adaptation to climate change, in addition to reducing greenhouse gases emissions. SDG 13 targets include improving resilience to climate-related hazards, increasing knowledge about climate change, as well as enhancing early warning. This will enable us to achieve our goal of limiting global temperature rise below 1.5 degrees Celsius.
The impacts of climate change affect human systems, natural systems, and social systems globally. This includes a rise in temperature, changes in precipitation patterns, and ocean acidification. These are the result of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. It is necessary for countries to tackle the problem from different angles in order reverse climate change. Among other things, governments need to improve the effectiveness of their climate policies. Companies can contribute to the goals by reducing their carbon footprint, building resilience in their operations, and scaling up their low-carbon products and services.
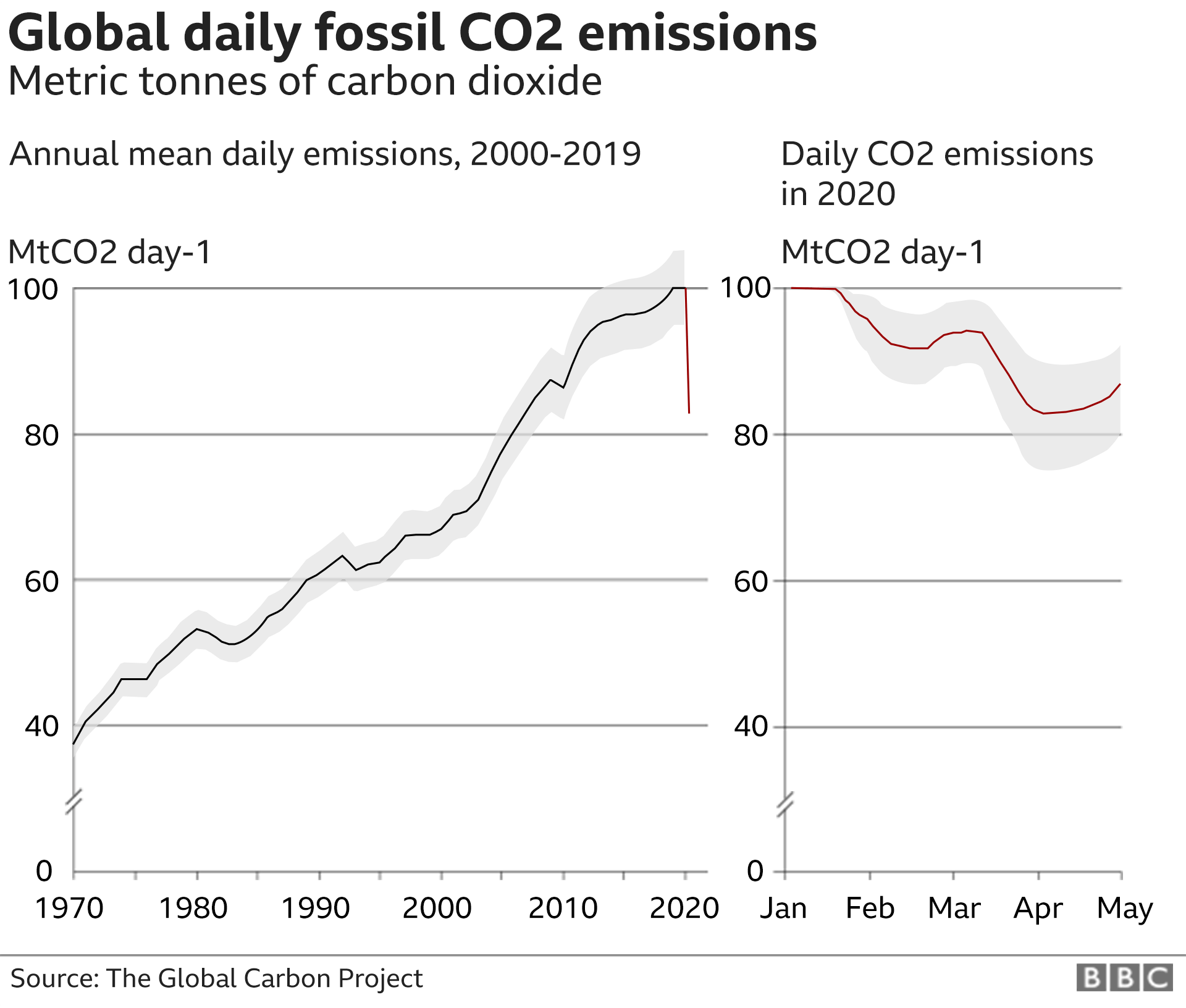
Despite increasing recognition of the necessity to address climate change, progress towards SDG 13 is mixed. Many of the indicators show progress, while others demonstrate that current commitments are insufficient to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. These results were derived from a disaggregated analysis on the Sustainable Development Goals. Countries should be focusing on energy efficiency at end-of-use, switching to renewable energy sources, and ensuring climate protection in national policies. These actions may bring short-term benefits, but they could take some time to pay off.
The SDG 13 monitoring reports, published in March 2016, identify indicators and show how countries are progressing towards these goals. The report also highlights possible links between the goals. The ability to increase the resilience of forests to climate change could help countries achieve their goals. A greater investment in the management and protection of forests can help improve the ability of communities to adapt to the effects of climate changes. Unsustainable forest exploitation could hinder synergies between SDG and forest conservation.
Currently, only 3 per cent of climate finance is dedicated to forest actions. Improved forestry and land management can help reach 20% of the Paris Agreement's targets. However, these actions will require long-term funding. Therefore, it is vital for countries to work with their local communities and others to reach these synergies. This will increase the chances of reaching the Paris Agreement's goals if these gaps are closed.
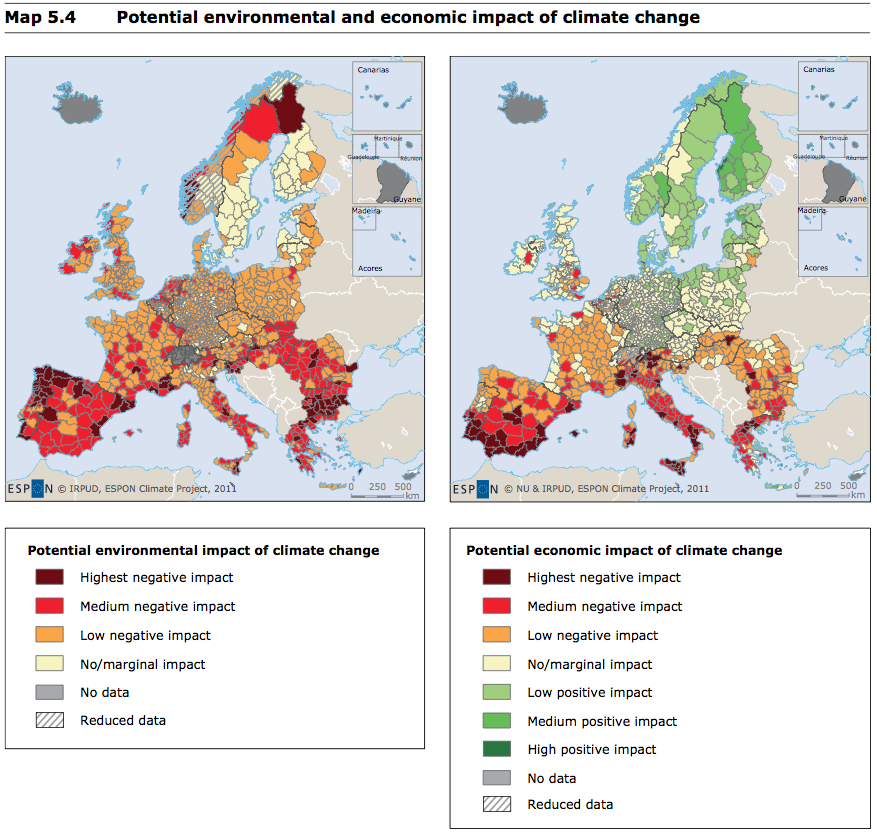
Despite the potential dangers of climate change, more countries are taking measures to adapt. These measures include improved agricultural practices, flood protection, and adaptation of agricultural techniques. Other adaptation measures include adaptation of economic activities, building knowledge and capacity for responding to climate change. Adaptation is crucial to achieve the SDGs as well as other global development goals.
All countries are affected. However, the extent of the impacts will depend on the size of the population, the economy, and the region. Some regions will suffer more from the effects of climate changes than others. The negative effects of climate change are evident in the groundwater supply, where the saline intrusions to the groundwater aquifers have a detrimental effect. Additionally, rising sea levels will have an adverse effect on freshwater supplies and will lead to saline contamination in coastal communities.
FAQ
What can be done to reduce or mitigate the effects of climate change?
There are many measures you can take to mitigate and reduce the impacts of climate change. These include reducing greenhouse emissions by using greener energy sources and better energy practices. It is important to increase public awareness about climate change as it makes people feel accountable for their actions.
How does climate change affect the world's oceans and marine life?
What are the effects of climate change on oceans and marine life around the globe?
Since its inception climate change has significantly affected the world's oceans as well as the marine life associated with them. Constant oceanic heat from the depletion in the ozone layer causes major disruptions in marine ecosystems. This leads to coral bleaching, and decreases in species.
Climate change may also be responsible for extreme sea level rises and more unpredictable weather conditions, which can prove to be fatal to coastal areas. Changes in temperature can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels, which could cause "dead zone" conditions in which marine life is scarce.
Ocean acidification is also being caused by excessive carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Ocean acidification causes an increase in pH which affects the vital functions of animals such as crabs, clams, and oysters that cannot adapt to changing conditions.
The effects of higher temperatures on natural habitats can be altered by shifting their geographical locations or shrinking them all together. This could lead to certain species becoming uninhabitable. An increase in ocean pressure can cause a drastic imbalance between predators & prey and lead to the extinction of many species.
The impacts of climate change have rippled through entire ecosystems. They impact multiple species either directly or indirectly through evaporation, decreasing water volumes, or sharp temperature changes. This could jeopardize any sustainable development for fishing and other maritime activities. Global climate change continues to wipe out entire species of life on Earth, transforming our future lives not only on the land but also deep below the oceans' surface.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
Greenhouse gasses are key to climate change. They act as an invisible blanket that wraps around the Earth, trapping heat radiation and warming it. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. As more heat enters the atmosphere from these activities, it leads to increased temperatures and extreme weather.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Important contributors are also methane and nitrousoxide (N2O), as well fluorinated gases (Fgases).
Human activities have caused a significant increase in greenhouse gas concentrations since preindustrial times. This has led both to global warming and an increase worldwide in temperatures, as well as increased ocean levels. It is also causing drastic changes, such as increased storms, droughts, melting glaciers and rising ocean levels.
To reduce further damage caused by climate change, human beings need to decrease their greenhouse gas emissions. We can do this by shifting away from fossil fuels in favor of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will help lower atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and create a healthier environment for all life on Earth.
How can the energy sector be involved in climate change?
The energy sector is a major contributor to climate change. The burning of fossil fuels is a primary source of global warming, caused by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, trapping heat, and leading to an increase in average temperatures on Earth.
To address this issue, energy sources must transition away from carbon-emitting fuels like coal and natural gaz and instead turn to renewable energy sources like solar, geothermal, wind, and other renewable sources. This change can be made by government policy, incentives, and investments in innovative technology, such as hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households will be able to reduce their carbon emissions and lower their electricity bills if they invest in infrastructure that supports renewable sources.
Other options include switching away from petroleum-fueled cars, moving towards electric vehicles, and public transport. Governments have the power to encourage and support investment in cleaner modes for transportation.
To reduce carbon footprints, companies should adopt green business practices. For example, better insulation in offices and production facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives should be championed at all levels, not just at company level but also at government. Raising taxes on pollution products encourages individuals and businesses to stop using harmful practices. While this may be a financial outlay for polluters, providing vouchers for or subsidy for low-carbon products can create a continuing market to support sustainability efforts. This is why tackling climate changes requires both private industry as well as private citizens to make a difference. By switching to green energy and adopting environmentally friendly practices, we can help to ensure that the future generations of people are affected positively.
What is the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change can have many impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. Changes in the hydrological cycles can also have an impact on water availability for species that live in aquatic environments.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. Up to 30% of all animal species could be extinct by 2050 due to climate change, which would lead to further losses in ecological communities.
Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity and human societies, as well as to ecosystems that provide food, water, timber, or other services. It is essential to mitigate its effects at all levels. Future damages must be avoided by careful management.
What are some possible solutions to climate change, and how effective are these solutions?
Climate change has become one of the most urgent issues of our time. It requires government, businesses and citizens to pay attention. A disrupted climate system is evident by rising temperatures, extreme weather events and increased sea levels. Numerous solutions have been suggested to deal with this phenomenon. They include technological solutions as well as behavioral changes and geoengineering.
Technological Solutions. There are many solutions to climate change that have been developed through technological changes. These include renewable energy sources like solar power and wind power that provide reliable sources for clean energy while causing minimal harm to the environment. Electric cars powered by renewable energy could significantly reduce air pollution in cities by replacing petrol vehicles. Other technological solutions include projects to increase carbon sequestration within trees and soil, as well coastal protection systems that protect vulnerable places from rising oceans.
Making behavioral changes: Simple changes to routines can make a huge difference in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting future climate disruption. For example, local production of goods and shorter supply chains can help reduce the emissions associated with transport costs. By using active or public transportation to transport your goods, you optimize your use of resources and bring down costs and air pollution. Also, insulation can be more cost-effective and help reduce the dependence on gas boilers in heating your home.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness of these solutions is dependent on how much producers will invest in green alternatives. Electric Cars are more costly than petrol versions, but economic incentives favoring these green solutions play an integral role. Incentivizing alternative solution use via policy measures is one step forward. However this requires regulatory bodies willing to engage the players further.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint & Fight Climate Change
You can reduce your carbon footprint while helping to combat climate change by taking several steps. You can reduce the amount of energy you use in your home by installing energy-efficient lighting and insulation. You can also save energy by unplugging electronics when not in use, using public transit, walking rather than driving, and turning down the temperature on your thermostat in the winter and summer months.
Second, recycling materials is a good idea. You can compost food scraps and not throw them away. Third, plant trees around your home for shade and natural cooling since vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. Consider purchasing products that are minimally packaged or sustainably labeled, such as organic cotton and FSC-certified timber. This will ensure that the forest is healthy.
Not only can you reduce your personal emissions but you can also support organizations like The Nature Conservancy Canada, Climate Change Solutions and Emissions Reduction Alberta.
All of us can make small changes to our daily lives and help combat climate change.