
A new report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has provided a detailed description of the impacts of climate change on the planet. It found that if global temperatures are to stay below 1.5 degrees Celsius (C) and to avoid dangerous consequences, nations would need to drastically reduce their anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions by 2030.
The report identifies five key risks. These include drought, heat, storm surges, sea level rise, and coastal flooding. Below is the "burning firecrackers" chart which shows the severity of risks at various levels. Darker colors indicate greater stress levels.

Not only are there physical effects, but also socioeconomic ones. Increased risk of flooding and tropical cyclone surges will cause more people to be forced from their homes. This will increase the death toll from extreme weather events. The report also found that the population at risk of coastal climate hazards will grow to a billion people by 2050.
The report acknowledges that many of the climate change impacts are already happening, but the magnitude of these impacts is far greater than was previously believed. Many species have been forced to range shifts, with about half of the land animals and plants moving their ranges to areas that are more conducive to survival.
Climate change has had severe consequences for access to water and food, in addition to altering the ecosystems. Millions are currently experiencing food insecurity due to climate change. In addition, rising temperature and storminess is reducing water availability. A similar trend is observed in the displacement of more than eight million people worldwide due to natural disasters.
Over eight percent of terrestrial species are at high risk of extinction. This figure is predicted to rise to 13 percent at three degrees and to 15 percent at four degrees. Regional extinctions are also at higher risk.
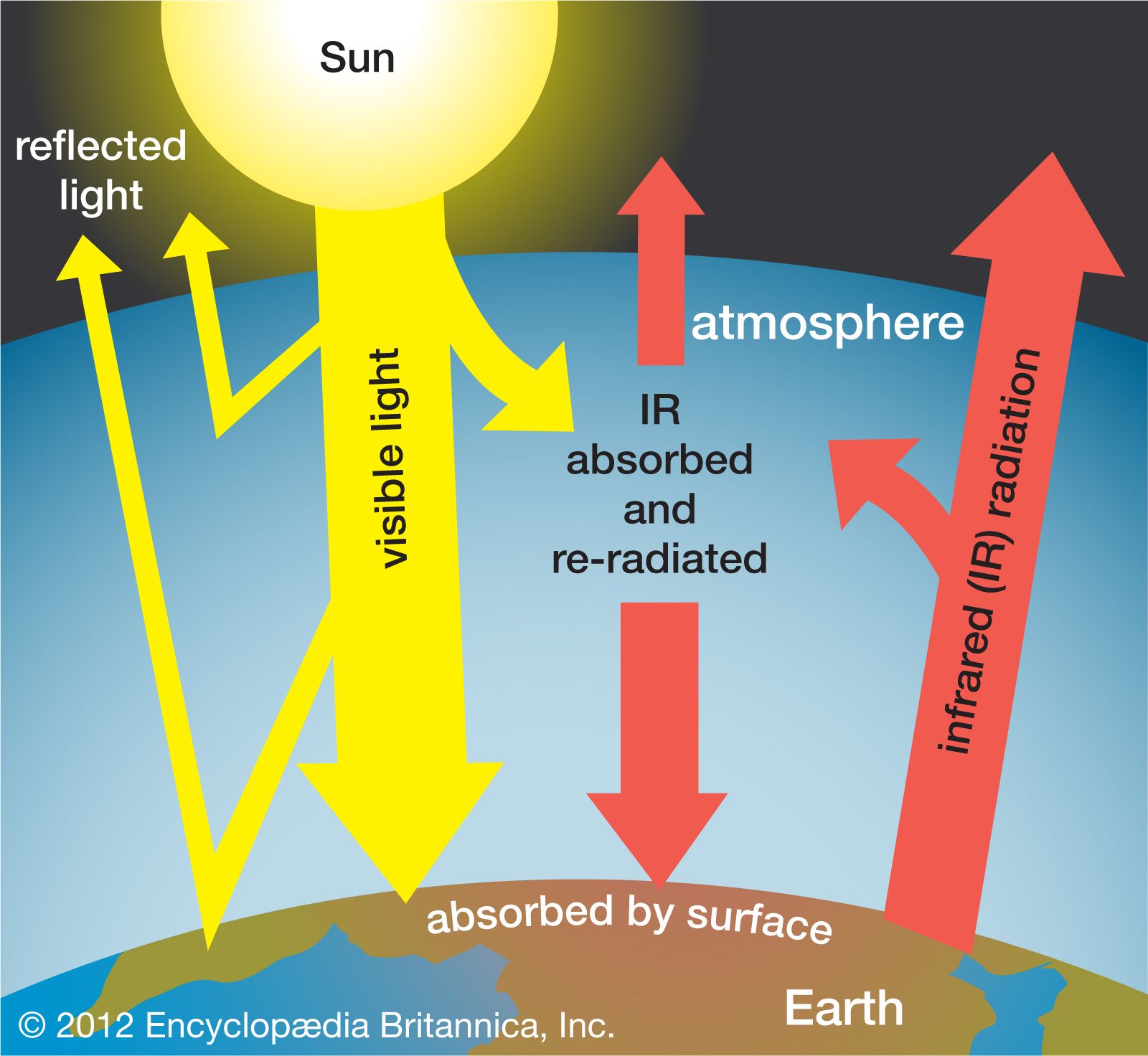
Increasing sea level will make flooding worse and could result in major cities losing their water resources. Oceans are heating, leading to hypoxia. This will make it less possible for marine microbes absorb oxygen. In addition, melting Arctic permafrost can release more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
A key threat to agricultural production is drought. At two degrees, agricultural drought is projected to be 150 to 200% more likely. Also, agricultural yields will likely decrease by 5-10%. This could lead to the loss of zinc and other essential nutrients depending on how much CO2 is released.
Climate change can also have an impact on the availability of zinc, iron, and protein. According to research, a carbon equivalent increase in atmospheric CO2 could reduce zinc by 7%. The same goes for protein. A CO2 equivalent increase will reduce it by 4%.
These conclusions are based on data from five climate models around the world. These findings are compared with two emission scenarios, a low and high scenario. Each of them outlines different methods to achieve macro-level conditions by 2030.
FAQ
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change is due in large part to human activity. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This raises the already existing atmospheric levels of CO2 which acts as an "greenhouse gas", trapping heat from Earth's surface and increasing temperatures. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Trees that sequester atmospheric CO2 in their trunks during photosynthesis are destroyed by deforestation. Cutting down forests also increases albedo - the amount of reflected solar radiation coming back into space - reducing solar heat absorption by the earth's surface thus promoting excessive warming at the global level. It also reduces the quality of local air, with deforestation being permanently linked to respiratory problems.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Large amounts of methane gas are released by animal waste due to its richness in methane bacteria. Eating less or none of these products can reduce global warming.
In conclusion, although human activity has had a devastating impact on our environment for centuries, technological advancements have enabled us to focus our minds towards the future. Instead of relying on carbon-emitting heavy industry, we can use green innovation to create eco-friendly efforts that combat climate change effectively and ensure everyone's safety.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Climate change is already having a wide range of sweeping effects on the environment and societies all over the world. As global temperatures rise, this trend is likely to intensify in the near term.
One of the most widespread effects of climate change is the rising ocean levels due to melting of ice caps. This results in coastal erosion and increased flooding risks for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Many countries are experiencing extreme weather events, such as droughts or heatwaves as a result climate change. These events lead to massive destruction of homes, businesses, and even the loss of whole communities. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
Wildfires caused by climate change also increasingly occur more frequently than they did before with devastating results both for habitats and people living nearby who may find their lives at risk due to poor air quality when these fires spread smoke across affected areas.
These dramatic changes in living conditions can often lead to displacement and even refugee crisis when people leave their homes voluntarily or involuntarily due to their changing climate.
People with respiratory diseases such as asthma are particularly vulnerable to dust storms from increased aridity. Pest infestations will increase due to higher temperatures - a phenomenon called the 'greenhouse bug'. This can further impact global food insecurity as fewer crops are available with poorer nutritional qualities, potentially creating additional hardships for marginalized populations that otherwise would be barely able to make ends meet.
What is the current climate like? How is it changing?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Temperatures are increasing dramatically due to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide, which is leading to heat waves, droughts and changes in rainfall patterns.
These changes already have a profound impact upon ecosystems around the globe and are causing extinctions as well as disruption of habitats. They are also threatening millions of people's lives and livelihoods, particularly in areas where there is already resource scarcity.
The number of extreme weather events - such as cyclones, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires - has been steadily growing over time due to higher average surface temperatures caused by human activity. As temperatures rise, this trend will likely continue.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also creating social inequalities bydisproportionately affecting marginalized populations that don't have the knowledge and resources necessary to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. We must all work together now to stop further disruptions and destruction from climate change.
What are the possibilities for new technologies to combat climate change?
This global problem is a huge challenge that new technologies can address. Advances in applied science make it possible to move to a more sustainable future.
Carbon capture and sequestration are two methods that can be used to lower greenhouse gas levels. Enhanced agricultural practices can reduce livestock emissions and soil degradation. Smart grid technology can be combined with existing power infrastructure to increase efficiency. Additionally, improved building design can reduce energy consumption.
A new generation of synthetic biology techniques allows scientists to develop organisms capable of converting green fuels such as the CO2 laser into biofuel or other feedstock. If the market shifts away from petrol-based cars to zero-emission electric vehicles powered by clean sources, this could transform transportation.
Finally, increasing investment in digital tech and AI can enable people to access data across borders and help them make more informed consumption decisions. Understanding our contribution to carbon production is crucial for us all to be better stewards.
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Temperature, precipitation and sea level changes increase pressure on already finite resources. Already fragile ecosystems are being destroyed by floods or droughts. Rising temperatures can result in a reduction in crop yields. This will be disproportionately detrimental to poorer communities who are facing food insecurity. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heatwaves, can cause the destruction of infrastructures and displacement of people, which further perpetuates economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. A rise in sea levels and extreme weather events will lead to increased flooding. This could put lives at risk in coastal regions, where there is often a lack of emergency services or infrastructure. These risks can be mitigated by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, other measures may be required such as better management of freshwater resources or easier access to healthcare facilities that aid in the prevention of diseases like malaria.
What is the current state of international efforts to address climate change?
The current international climate change effort is characterized by unprecedented unity and momentum. Countries all around the globe are increasingly joining forces to find solutions to climate change.
The Paris Agreement has been a catalyst for global action. Individual countries can set voluntary targets for reducing their carbon emissions by using the framework provided by the Paris Agreement. In addition, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change provides political guidance as well as piloting new initiatives such carbon market mechanisms.
Other regions are seeing progress. The European Green Deal is a comprehensive legislation package that seeks to create a European economy with sustainability as its core. Countries on the African continent also have committed to The African Renewable Energy Initiative, which aims increase Africa's participation in global renewable energy production.
There are many sectors and industries that are taking action in addition to policy development. Cities are making active transitions toward sustainable public transport systems, while society overall is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Businesses are innovating technologies which reduce emissions, while investors move their capital from fossil fuels to renewables.
Through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR), the 2021 Guidelines, the rich countries that are members of the OECD committee have agreed to common standards for reporting their national climate change actions.
All these efforts are a sign of the unprecedented importance given to climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
How does climate change affect the world's oceans and marine life?
What is the effect of climate change upon the world's oceans?
Since its inception climate change has significantly affected the world's oceans as well as the marine life associated with them. Constant oceanic heat from the depletion in the ozone layer causes major disruptions in marine ecosystems. This leads to coral bleaching, and decreases in species.
Unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms are also linked to climate change, leading to extreme surges in sea levels that can prove deadly for coastal areas. Temperature changes can also cause water levels to drop, causing "dead zones", areas where there is less marine life.
Ocean acidification is also a result of excess carbon dioxide that has built up in the oceans. This is due to climate change. Ocean acidification alters the pH balance, which makes it impossible for some animals, like oysters, crabs, and clams to adapt.
Higher temperatures can alter the natural habitats of certain species by changing their locations or shrinking them, making them uninhabitable. The increase in ocean stresses accelerates the already high rates of extinction worldwide. This can lead to a severe imbalance among predators and prey, which could ultimately lead to complete extinction.
The impacts of climate change have rippled through entire ecosystems. They impact multiple species either directly or indirectly through evaporation, decreasing water volumes, or sharp temperature changes. This could jeopardize any sustainable development for fishing and other maritime activities. Climate change is transforming the future of all life forms on our planet, not just those living on land but those living below the ocean surface.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Carbon Footprint, Fight Climate Change
There are many steps that you can take to reduce your carbon footprint and help fight climate change. First, invest in energy-efficient appliances and lighting. You can also save energy by unplugging electronics when not in use, using public transit, walking rather than driving, and turning down the temperature on your thermostat in the winter and summer months.
Second, recycling materials is a good idea. You can compost food scraps and not throw them away. Third, plants trees around your house for shade and natural cooling. The air absorbs carbon dioxide through the vegetation. Finally, you can consider buying products with minimal packaging and sustainable labelings like organic cotton or FSC wood. These certifications indicate that it has been sustainably managed over a long period of time to preserve forest health.
You can help reduce your personal emissions by supporting organizations such as Emissions Reduction Alberta, Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute and The Nature Conservancy Canada. These organizations work to lower emissions through clean energy investments. They also support international initiatives such ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability's Urban Sustainability Strategies program.
Everyday changes can be made to help fight climate change.